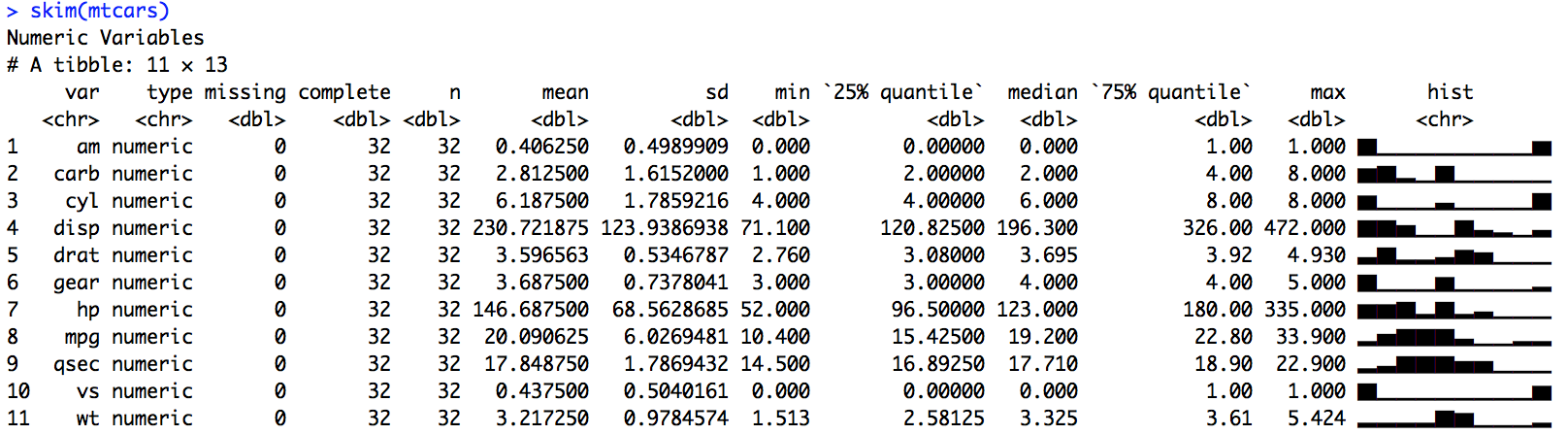
Following up on Stefanie’s recap of unconf 17, we are following up this entire week with summaries of projects developed at the event. We plan to highlight 4-5 projects each day, with detailed posts from a handful of teams to follow.skimr Summary: skimr, a package inspired by Hadley Wickham’s precis package, aims to provide summary statistics iteratively and interactively as part of a pipeline.