The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is a warehouse of species occurrence data - collecting data from a lot of different sources. Our package rgbif allows you to interact with GBIF from R. We interact with GBIF via their Application Programming Interface, or API. Our last version on CRAN (v0.3) interacted with the older version of their API - this version interacts with the new version of their API.
We are building a taxonomic toolbelt for R called taxize - which gives you programmatic access to many sources of taxonomic data on the web. We just pushed a new version to CRAN (v0.1.5) with a lot of changes (see here for a rundown). Here are a few highlights of the changes.
We have previously written about creating interactive maps on the web from R, with the interactive maps on Github. See here, here, here, and here. A different approach is to use CartoDB, a freemium service with sql interface to your data tables that provides a map to visualize data in those tables.
Previously on this blog we have discussed making geojson maps and uploading to Github for interactive visualization with USGS BISON data, and with GBIF data, and on my own personal blog. This is done using a file format called geojson , a file format based on JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) in which you can specify geographic data along with any other metadata.
I recently attended ScienceOnline Climate, a conference in Washington, D.C. at AAAS. You may have heard of the ScienceOnline annual meeting in North Carolina - this was one of their topical meetings focused on Climate Change. I moderated a session on working with data from the web in R, focusing on climate data. Search Twitter for #scioClimate for tweets from the conference, and #sciordata for tweets from the session I ran.
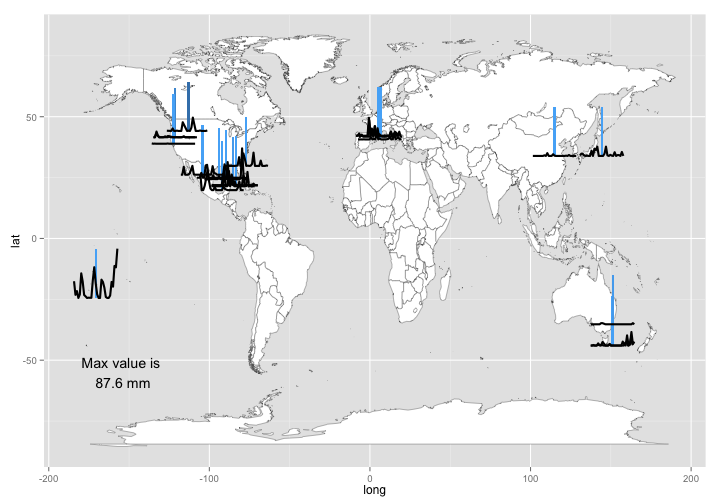
We have started a new R package interacting with NOAA climate data called rnoaa . You can find our package in development here and documentation for NOAA web services here. It is still early days for this package, but we wanted to demo what you can do with the package.
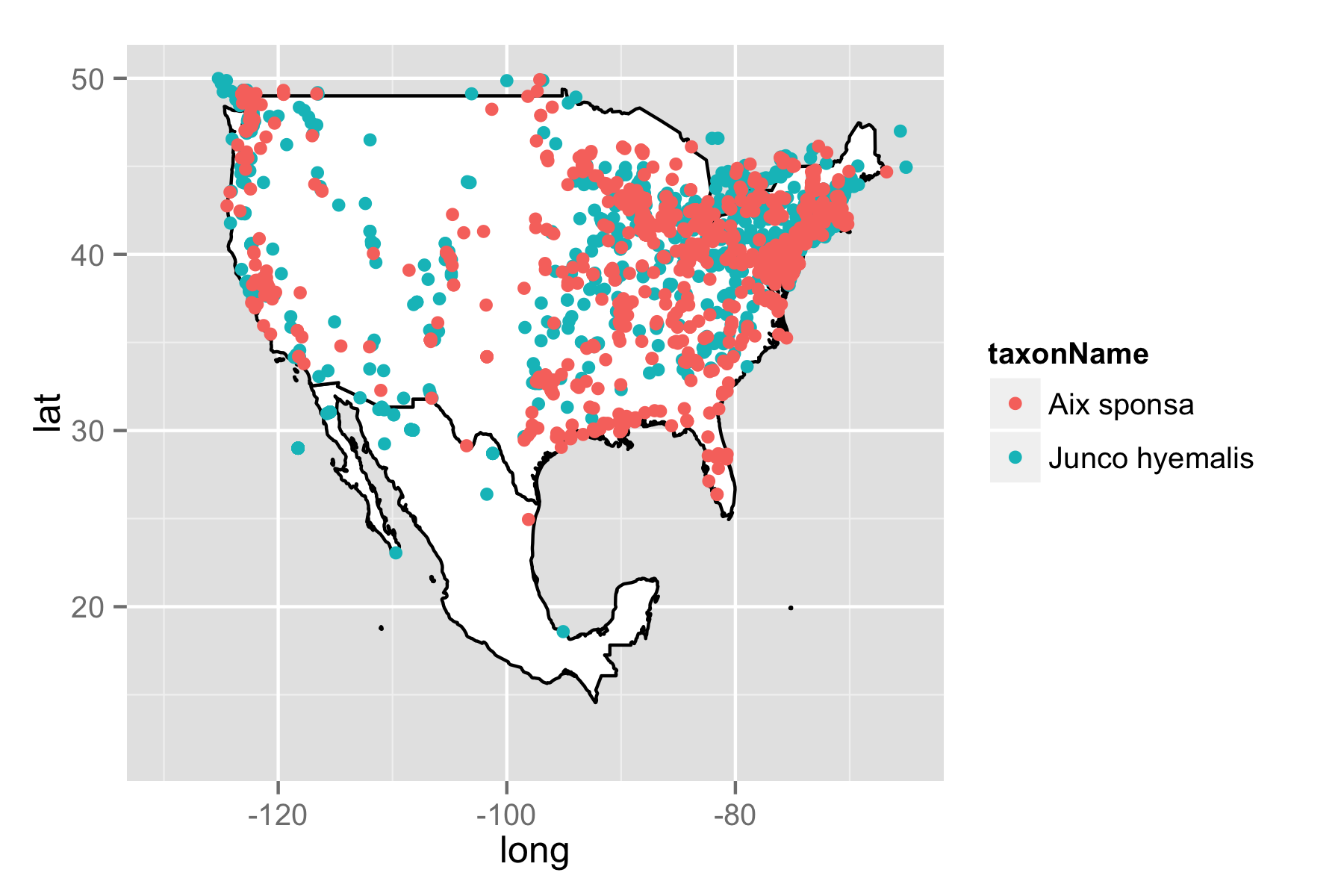
One of our primary goals at ROpenSci is to wrap as many science API’s as possible. While each package can be used as a standalone interface, there’s lots of ways our packages can overlap and complement each other. Sure He-Man usually rode Battle Cat, but there’s no reason he couldn’t ride a my little pony sometimes too. That’s the case with our packages for GBIF and the worldbank climate data api.
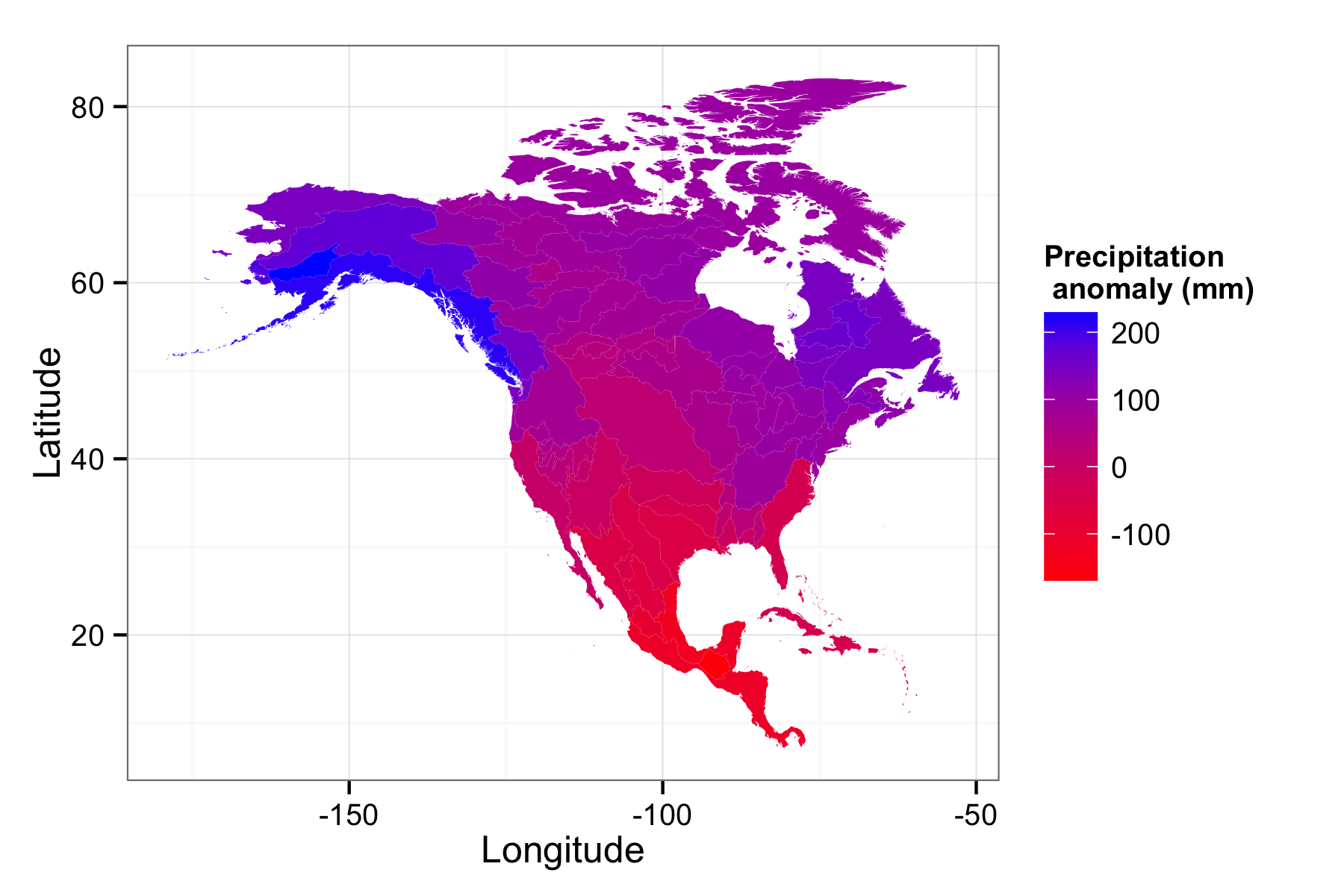
A recent video on the PBS Ideas Channel posited that the discovery of climate change is humanities greatest scientific achievement. It took synthesizing generations of data from thousands of scientists, hundreds of thousands (if not more) of hours of computer time to run models at institutions all over the world. But how can the individual researcher get their hands of some this data?
Previously on this blog and on my own personal blog, I have discussed how easy it is to create interactive maps on Github using a combination of R, git and Github. This is done using a file format called geojson , a file format based on JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) in which you can specify geographic data along with any other metadata.
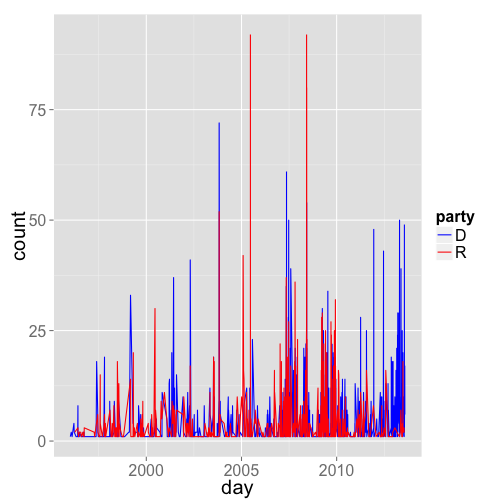
We have a number of packages for getting species occurrence data: rgbif and rbison. The power of R is that you can pull down this occurrence data, manipulate the data, do some analyses, and visualize the data - all in one open source framework. However, when dealing with occurrence data on maps, it is often useful to be able to interact with the visualization.